Forecast details
Wind
Wind direction
The arrow indicates wind direction:
 — North wind (blows from north to south).
— North wind (blows from north to south). — South wind (blows from south to north).
— South wind (blows from south to north). — West wind (blows from west to east).
— West wind (blows from west to east). — East wind (blows from east to west).
— East wind (blows from east to west).
Wind speed
Measured in meters per second (m/s) using an anemometer.
Meteum shows the wind speed at a height of 10 m from the Earth's surface.
- Difference between the atmospheric pressure and temperature in different layers of the atmosphere.
- Uneven heating of the underlying surface.
- Terrain features (mountain, forest, or city).
| Wind speed, m/s. | Wind force |
|---|---|
| 0 | Calm |
| 1-5 | Light |
| 6-10 | Moderate |
| more than 10 | Strong |
| Wind speed, m/s. | Wind force |
|---|---|
| 0 | Calm |
| 1-5 | Light |
| 6-10 | Moderate |
| more than 10 | Strong |
For more information about wind speed ranges, see the Beaufort scale . This is an international scale for measuring wind speed on land and at sea.
Humidity
Shows the amount of water vapor in the air. Humidity is measured 2 m above ground.
High humidity increases the likelihood of dew or fog.
- Moisture transfer by air flows.
- Water evaporation.
The forecast shows the relative humidity of the air, i.e. the amount of water vapor in the air as compared with the maximum amount of water that the air could possibly hold at the current temperature.
Humidity is displayed in the weather card on the service's homepage and in the detailed forecast.
Pressure
Pressure is affected by atmospheric circulation.
When a cyclone is coming, the atmospheric pressure decreases, and when an anticyclone is coming, the pressure increases.
- If the air is moving counterclockwise, it's a cyclone.
- If the air is moving clockwise, it's an anticyclone.
| Difference from the norm for the region, mmHg | Pressure value |
|---|---|
| More than 20 below the norm for the region | Low |
| 10-20 lower than the norm for the region | Reduced |
| Within 10 above the norm for the region | Standard |
| 10-20 higher than the norm for the region | Increased |
| More than 20 above the norm for the region | High |
| Difference from the norm for the region, mmHg | Pressure value |
|---|---|
| More than 20 below the norm for the region | Low |
| 10-20 lower than the norm for the region | Reduced |
| Within 10 above the norm for the region | Standard |
| 10-20 higher than the norm for the region | Increased |
| More than 20 above the norm for the region | High |
Magnetic field
The magnetic field is affected by solar activity. When solar flares occur, a stream of particles reaches the Earth and impacts its magnetic field.
Researchers measure the state of the magnetic field with the Kp index. It shows the average deviation of the entire Earth's magnetic field from the norm calculated for three-hour intervals. The Kp index values range from 1 (quiet activity) to 10 (extreme magnetic storm).
In the service, the values of the Kp index correspond to the following verbal definitions:
| Kp index | State of magnetic field on the service |
|---|---|
| Less than 4 | Quiet |
| 4 | Unstable |
| 5 | Slightly disturbed |
| 6 | Disturbed |
| 7 | Magnetic storm |
| 8 or higher | Strong magnetic storm |
| Kp index | State of magnetic field on the service |
|---|---|
| Less than 4 | Quiet |
| 4 | Unstable |
| 5 | Slightly disturbed |
| 6 | Disturbed |
| 7 | Magnetic storm |
| 8 or higher | Strong magnetic storm |
You can see the state of the magnetic field in the detailed forecast. Meteum shows the current state of the magnetic field for the current day and the next three days. No forecast is made for subsequent days, as its accuracy is low.
Magnetic field disturbances may cause a communication blackout and power system failures. Some people may be affected by the force of a magnetic storm.
Feels like
The same temperature values can be perceived differently, depending on humidity, wind force, and other factors. For example, a temperature of –5° feels a lot colder when there's a strong wind, and a warm day feels hot if the humidity is high. That's why the forecast also displays a Feels like indicator. It shows how comfortable the weather conditions are.
When calculating the “feels like” temperature, the following is taken into account:
- Air temperature.
- Humidity.
- Wind speed.
- Solar radiation.
Daylight hours
The time from sunrise to sunset.
Meteum calculates daylight hours while taking into account atmospheric refraction, a phenomenon associated with light deflection and scattering. When light passes from the more dense layers of the atmosphere to the less dense ones (and vice versa), its speed changes and the sun rays deviate from a straight line. Atmospheric refraction is especially noticeable when the sun is near the horizon: when it is already below the horizon, you can still see the sun's disk.
Daylight duration increases due to atmospheric refraction.
You can see the sunrise and sunset time on the service's home page and in the detailed forecast. The detailed forecast shows daylight hours.
Water temperature
Shows water surface temperature.
Water temperature is only displayed for cities located near large water bodies. If the weather stations nearest to the city do not measure water temperature, Meteum calculates this indicator's value.
You can see the water temperature on the service's home page in the weather card and in the detailed forecast.
Air temperature
Shows the temperature in the shade at a height of 2 m above the Earth's surface.
- Located at a height of 2 m from the ground.
- Open to the wind.
- Not affected by direct sunlight.
Household thermometers are not always installed according to these rules, so their readings may differ from the temperature on Meteum.
UV index
Describes the level of solar radiation at the surface of the Earth and whether it's dangerous to humans.
- Seasonal activity of the sun.
- The sun's position relative to the latitude, horizon, and sea level.
- The condition of the ozone layer above the area.
- Aerosol concentration in the air.
- Terrain reflectivity.
- Type of clouds.
- How to protect yourself from solar radiation
-
UV index value WHO recommendations 0-2: low
There is minimal risk of sunburn, even if your skin is sensitive. 3-7: moderate Try to stay in the shade from 12:00 to 16:00. Use sunscreen with SPF 15-30.
Wear a hat and a long-sleeve shirt.
More than 8: very high Avoid being outside from 12:00 to 16:00.
Use 50 SPF sunscreen.
Wear protective clothing and sunglasses.
UV index value WHO recommendations 0-2: low
There is minimal risk of sunburn, even if your skin is sensitive. 3-7: moderate Try to stay in the shade from 12:00 to 16:00. Use sunscreen with SPF 15-30.
Wear a hat and a long-sleeve shirt.
More than 8: very high Avoid being outside from 12:00 to 16:00.
Use 50 SPF sunscreen.
Wear protective clothing and sunglasses.
- Where to find the UV index
-
The current UV index value is displayed on the service's home page.
You can find out the UV index value for the next four days in the detailed forecast.
Moon phase
Shows how much the moon is illuminated by the sun.
On the service's homepage, in the forecast for today, you can see textual information about the phase of the moon.
In the detailed 10-day forecast, the phase of the moon is displayed as an image. The yellow portion of the disk shows the visible part of the moon, while the dark-gray one reflects its invisible part.
| Icon | Moon Phase | Approximate time when the moon is visible in the sky |
|---|---|---|
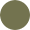 | New moon | Not visible |
 | Waxing crescent | 09:00–21:00 |
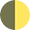 | First quarter | 12:00–00:00 |
 | Waxing gibbous | 15:00–03:00 |
 | Full moon | 18:00–06:00 |
 | Waning gibbous | 21:00–09:00 |
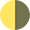 | Last quarter | 00:00–12:00 |
 | Waning crescent | 03:00–15:00 |
| Icon | Moon Phase | Approximate time when the moon is visible in the sky |
|---|---|---|
 | New moon | Not visible |
 | Waxing crescent | 09:00–21:00 |
 | First quarter | 12:00–00:00 |
 | Waxing gibbous | 15:00–03:00 |
 | Full moon | 18:00–06:00 |
 | Waning gibbous | 21:00–09:00 |
 | Last quarter | 00:00–12:00 |
 | Waning crescent | 03:00–15:00 |
- 0 — New moon.
- 0.5 — First or last quarter.
- 1 — Full moon.
The service uses the method described by Jean Meeus in his book “Astronomical Algorithms” which is based on the calculation of the Sun's illumination factor of the Moon's disk. This factor depends on the selenocentric distance of the Earth from the Sun (phase angle).
When calculating the phase angle, the distances from the Earth to the Sun and from the Earth to the Moon are taken into account, as are the longitude and latitude of the lunar subsolar point.
Depending on the day of the sidereal month (the period during which the Moon makes a complete revolution around the Earth), the distance from the Earth to the Moon and from the Earth to the Sun varies. The distance from the Earth to the Sun is considered to be equal to one astronomical unit (1 AU), which is 149,971,520 km, while the distance from the Earth to the Moon and the longitude and latitude of the lunar subsolar point are calculated for certain dates and times.
The illumination factor can take values from 0 to 1:
You can determine whether the Moon is growing or waning by calculating the factor for two days. If it increases for the following day, the Moon is waxing; otherwise, the Moon is waning.